In this Article, we’ll delve into Scan to BIM process, benefits, and real-world applications, while exploring how Titan BIM is leading the charge with AI-driven innovation.
What is Scan to BIM?
Scan to BIM is the process of converting point cloud data captured from laser scans or photogrammetry into a detailed 3D BIM model. This model represents the as-built condition of a building or infrastructure, providing accurate data for design, analysis, and decision-making throughout the lifecycle of a project.
At its core, Scan to BIM bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds. Unlike traditional surveying methods, Scan to BIM provides unmatched accuracy and results that are easy to visualize and share across teams, making it an invaluable tool in the modern AEC workflow.
Why is Scan to BIM Important?
- Accuracy: Traditional methods often leave room for manual errors. it ensures that every dimension and feature is captured precisely.
- Visualization: The 3D model created in BIM software provides an immersive way to analyze and study existing buildings or sites.
- Collaboration: All stakeholders—from engineers to surveyors—can use the same data-rich model, streamlining communication and decision-making.
How Scan to BIM Works?
The Scan to BIM workflow can be broken down into several steps, each critical to the accuracy and success of the final model. Here’s an overview of how it works:

- Data Capture with Laser Scanning
High-precision laser scanners (also known as LiDAR) are deployed to gather data on the structure or project site. These scanners produce a “point cloud,” a collection of millions (or even billions) of data points that represent the physical environment with incredible detail.

- Data Processing and Cleaning
Once the point cloud is captured, the data is processed and cleaned using specialized software to remove noise or irrelevant information. This ensures the resulting dataset is more manageable and usable for further modeling.

- Converting Point Cloud to BIM
The processed point cloud is imported into BIM modeling software such as Autodesk Revit or ArchiCAD. Here, a 3D model is created to reflect the geometric and spatial properties of the existing structure.

- Integration into the Project
The final BIM model is ready to be used for various applications, ranging from renovation projects and clash detection to asset management and planning.
This seamless workflow allows AEC professionals to shift from traditional 2D blueprints to a highly interactive digital twin of the project.
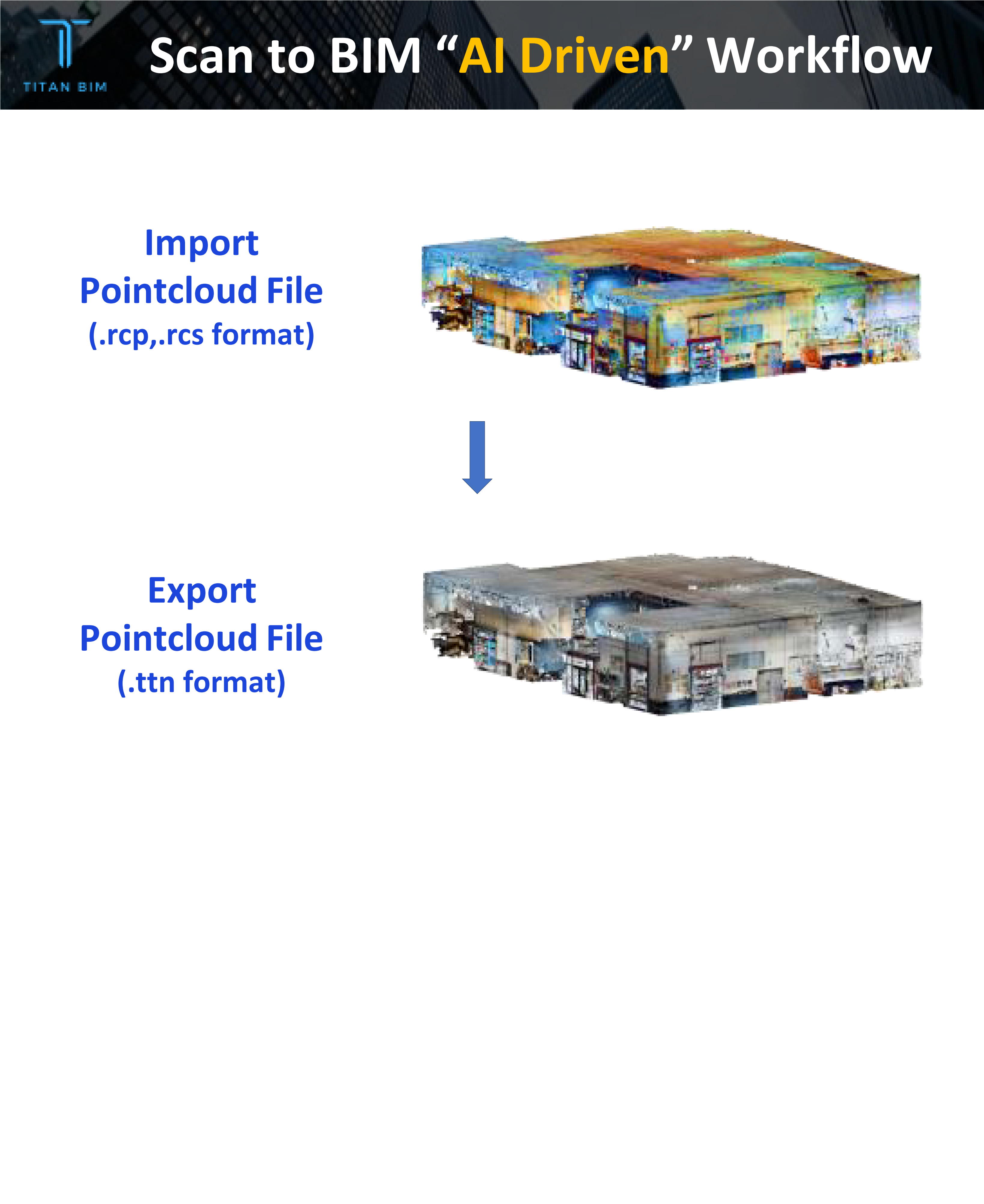
Pointcloud conversion to “TITANBIM native format”
We are converting scan file to our native format to operate it with our AI tool, require dense scan to work with it.
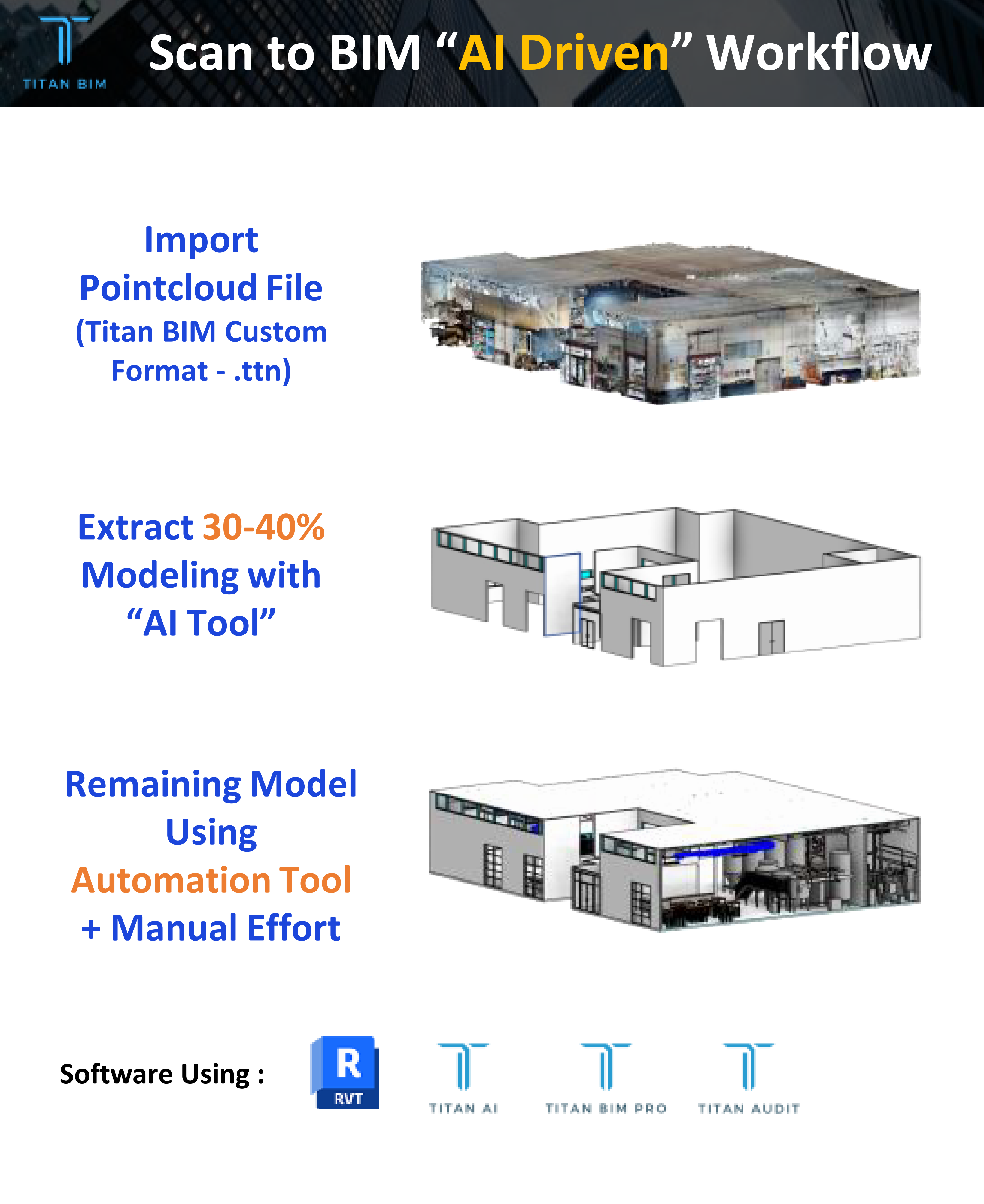
30-40 % Model Extraction by our “AI Tool”
Extraction of Walls, Doors, Windows by our AI Tool. Its still in progress, working with high quality scans only.
Remaining Model using our “Revit Automation Tool” & Manual Efforts
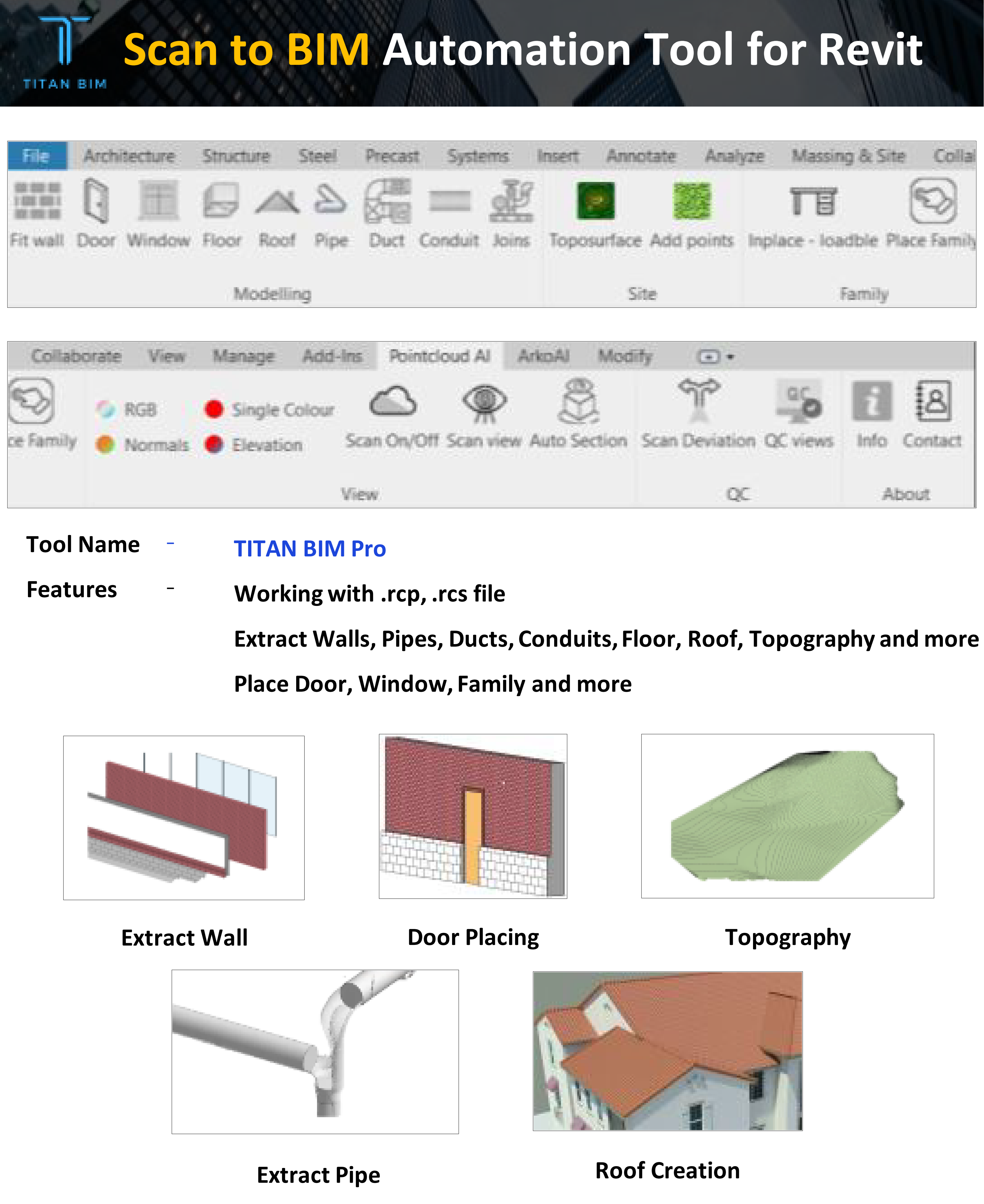
20+ Features in our “Revit Automation Tool”.
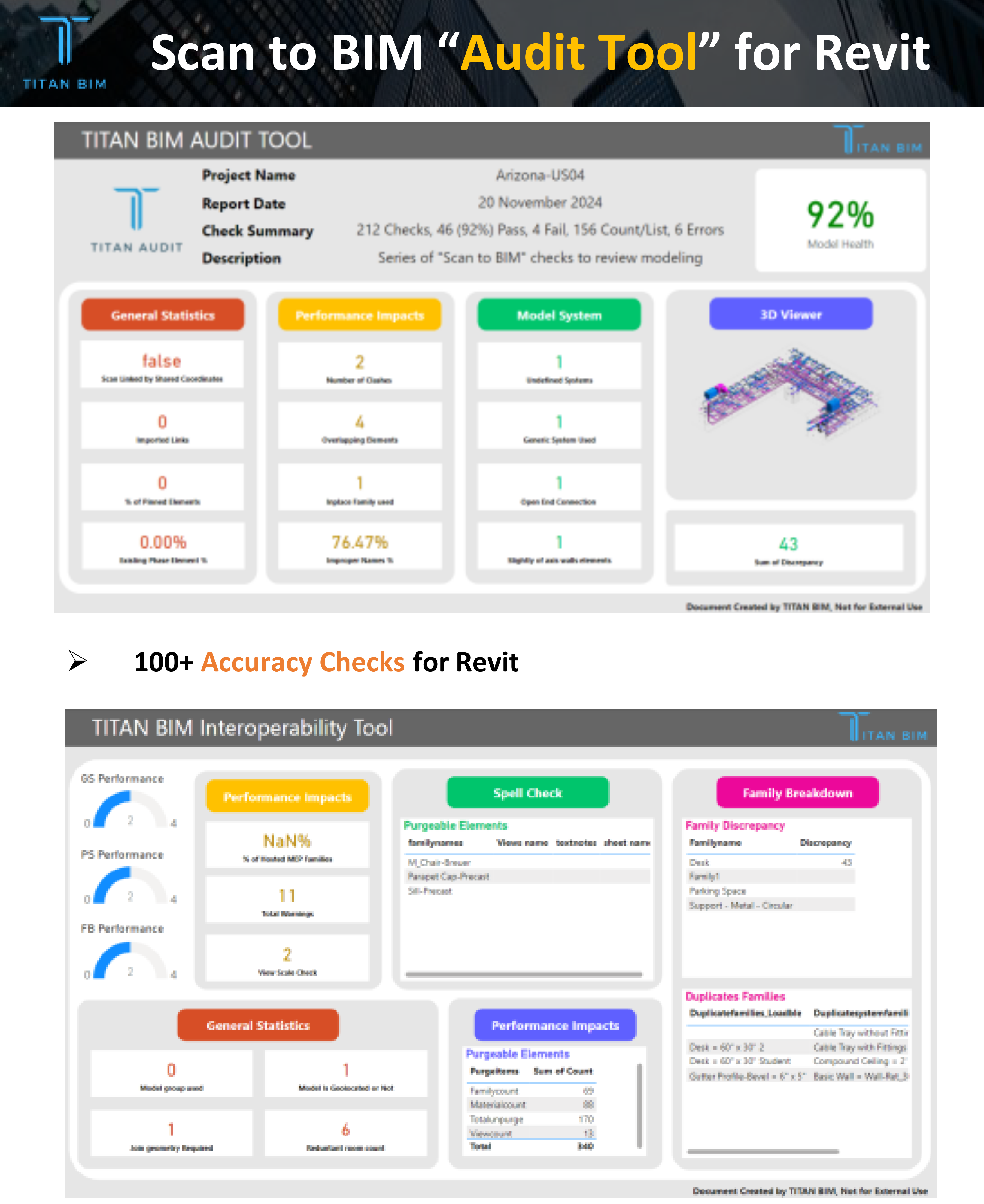
Model Audit through our “QC Audit Tool”
100+ Accuracy checks by our “TITAN Audit” Revit Tool
TITAN BIM Tool for Scan to BIM Projects
Benefits of Scan to BIM
- Enhanced Accuracy
Unlike manual measurements, which are subject to human error, laser scanning captures precise data that ensures the resulting BIM model reflects the actual site dimensions.
- Time and Cost Savings
By digitizing the surveying process, Scan to BIM reduces labor hours and costs associated with errors or rework. It eliminates discrepancies between “as-built” conditions and design models.
- Eases Renovation and Restoration
For renovation or historic preservation projects, Scan to BIM provides a detailed documentation of existing conditions, making planning more efficient.
- Supports Facility Management by Digital Twin Technology
Provides a digital twin for maintenance, operation, and lifecycle management.
- Reduced Rework
Minimizes costly errors by delivering reliable and accurate documentation.
- Supports Advanced Simulations
With accurate data, professionals can perform simulations for structural analysis, energy performance, and even virtual walkthroughs.
Challenges and Best Practices in Implementing Scan to BIM
Despite its benefits, Scan to BIM comes with certain challenges that professionals need to be aware of. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
Challenges
- High Initial Investment: Laser scanning equipment and software can be costly for smaller firms.
- Complex Learning Curve: It takes time for professionals to become proficient in handling and processing point cloud data.
- Data Overload: Processing large datasets of point clouds can be resource-intensive and may require high-powered computers.
Best Practices
- Start Small: Begin with smaller projects to gain familiarity with the tools and process.
- Invest in Training: Ensure your team is properly trained in both hardware usage and BIM software.
- Outsource When Needed: Partner with specialized firms for scanning or data processing to minimize upfront investment risks.
Adopting these best practices can ease the adoption curve, helping firms unlock the full potential of Scan to BIM technology.
Real-world Applications and Case Studies
Scan to BIM is revolutionizing how the AEC industry approaches projects across various applications. Here are some notable use cases:
- Historic Preservation
Architectural firms restoring heritage sites use Scan to BIM to create digital twins of monuments. For example, Scan to BIM was key in documenting Notre Dame Cathedral following the devastating fire in 2019.
- Renovations and Retrofits
Contractors often turn to Scan to BIM during renovation projects to capture accurate as-built conditions. For example, it has been used in retrofitting energy-efficient systems into older buildings.
- Infrastructure Projects
Civil engineers have applied it to large-scale infrastructure projects like tunnels, bridges, and airports to ensure precision, safety, and optimal resource management.
- Facility Management
For property managers, BIM models enhanced through scanning offer an up-to-date record of the facility, improving maintenance and operational decisions.
These real-world applications highlight the versatility and value of Scan to BIM technology, from small buildings to large-scale infrastructure.
The Future of Scan to BIM Technology
As technology advances, the future of Scan to BIM looks promising. Here’s what lies ahead:
- AI and Automation
With AI integration, the tedious task of manually converting point cloud data into usable 3D models may soon be automated, saving even more time.
- Integration with VR/AR
The integration of Scan to BIM technology with virtual and augmented reality tools will allow for real-time collaboration and visualization.
- Lower Costs and Accessibility
Falling hardware and software costs will make this technology accessible to smaller firms and independent professionals.
- Sustainability Focus
Scan to BIM will play a critical role in energy modeling and LEED certification, supporting sustainable design initiatives.
The horizon’s advancements will not only enhance efficiency but will also redefine the entire design and construction process in the AEC sector.













1 Comment
Excellent post! We will be linking to this great article on our site.
Keep up the great writing.